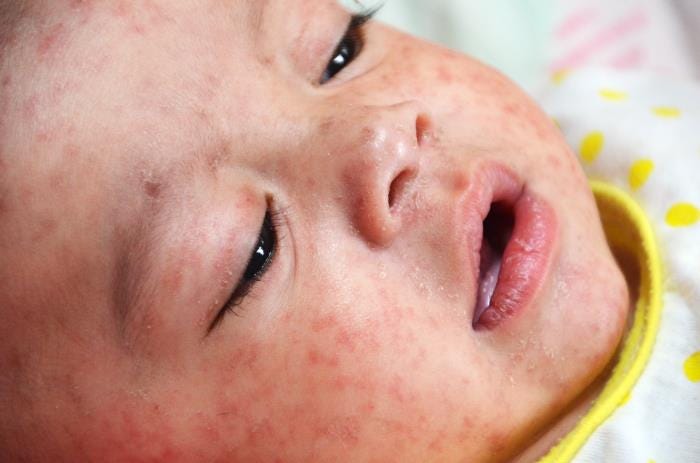
Measles outbreak worsens
March 5, 2025
Summary: Measles is exceptionally infectious, and declining vaccination rates raise the risk of broader outbreaks.
CDC, 2014
As of last week, there were 168 cases of measles reported in Texas and New Mexico. Most of these have been in unvaccinated children, and 22 have been hospitalized. One child has died of measles in the Texas outbreak. Vaccination rates are low in the impacted Texas county (80%). While the measles vaccine is 97% effective, some who have been vaccinated will have waning immunity and can get measles.
Measles is one of the most contagious airborne viruses, and is spread when someone who is infected exhales, coughs, or sneezes. Nine out of ten unvaccinated people without immunity who are in a room with a person with measles will be infected. The virus can remain viable for two hours in the air after an infected person leaves a room.
Measles generally leads to hospitalization in about one in five people and kills one to two of 1,000 who are infected.
Before the first measles vaccine was licensed in 1963, there were an average of 550,000 measles cases and 500 deaths reported annually in the U.S. The measles vaccine is safe and does not contribute to autism, based on multiple studies and decades of use.
Measles can cause an immediate or delayed encephalitis that kills or disables those who have had a measles infection. Measles infection also diminished preexisting antibodies to other infectious diseases, causing ”immune amnesia” in those who got measles and had not previously been vaccinated. Therefore, measles epidemics can also increase risk of illness and death from other infectious diseases.
Here are two epidemiologists who I regularly follow:
Your Local Epidemiologist (Katelyn Jetelina)
Force of Infection (Caitlin Rivers)
Implications for employers:
People who had measles in the past or have had two measles vaccinations are well-protected against measles.
Adults who are uncertain of their measles immunity status can either get two MMR vaccines a month apart or get a blood test to see if they are immune.
While MMR vaccines are generally given at 15 months of age, infants in areas with known cases can be vaccinated at 6 months. Measles is most dangerous in the youngest children.